Rebars are classified based on a certain amount of their tensile strength, which is called rebar tensile strength. Rebars produced in Iran (according to the Russian standard) are divided into four general groups: Rebar type: A1. A2. A3 A4
Rebar A1 (soft without tread): The first group are rebar A1, which is also known in class S240 in terms of classification and there is no tread shape on them. The yield strength and tensile strength are 240 and 360 MPa, respectively. Due to the low percentage of carbon in these rebars, its welding and forging capability is higher compared to other categories.
Rebars A2 (semi-rigid with simple tread): The next category is rebars A2 which are ribbed and are classified in class S340 in terms of classification. In fact, this rebar is an axis along the longitudinal axis and a series of turns are located in a spiral with respect to this longitudinal axis. These products are more durable than A1 rebars. The yield strength of these rebars is 340 and their tensile strength is 500 MPa. Due to the increase in carbine in this category of welding rebar is difficult to do.
Rebar A3 (hard with twisted tread): The third category is ribbed rebar with spiral tread shape. The shape of the beams in this rebar is fan-shaped (porch-shaped) in relation to the longitudinal axis and in terms of strength, they have higher resistance than rebars A1 and A2. The yield strength of these rebars is 400 and their tensile strength is 600 MPa. Due to the high carbon content of these rebars, welding on them is not allowed. The application of this product in the main rebars of the structure includes longitudinal rebars of beams and columns.
A4 rebar (hard with composite tread): The fourth category is ribbed rebar with composite shape. The shape of the treads in this rebar is composite and has a higher strength than the rest of the rebar, their yield strength and tensile strength are equal to 500 and 650 MPA, respectively. The welding ability of this category of rebars is less compared to other categories due to the high amount of carbon.
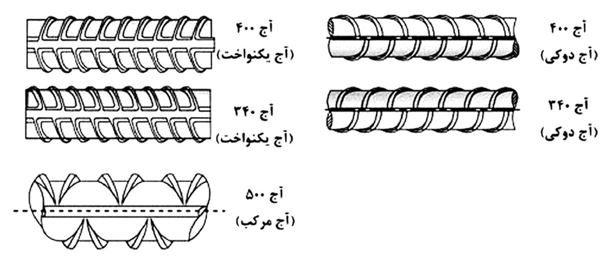

Table 1: Chemical composition of rebars

Table 2: Mechanical properties of rebars

Table 3: Equivalent standard

Table 4: Mechanical properties of coiled wire and industrial rebars
Foolad Persian Amir Trading Company was registered in the Companies Registration Office in Tehran on June 12, 2008 with the aim of supplying, distributing and supplying, importing, exporting and buying and selling all kinds of hardware.